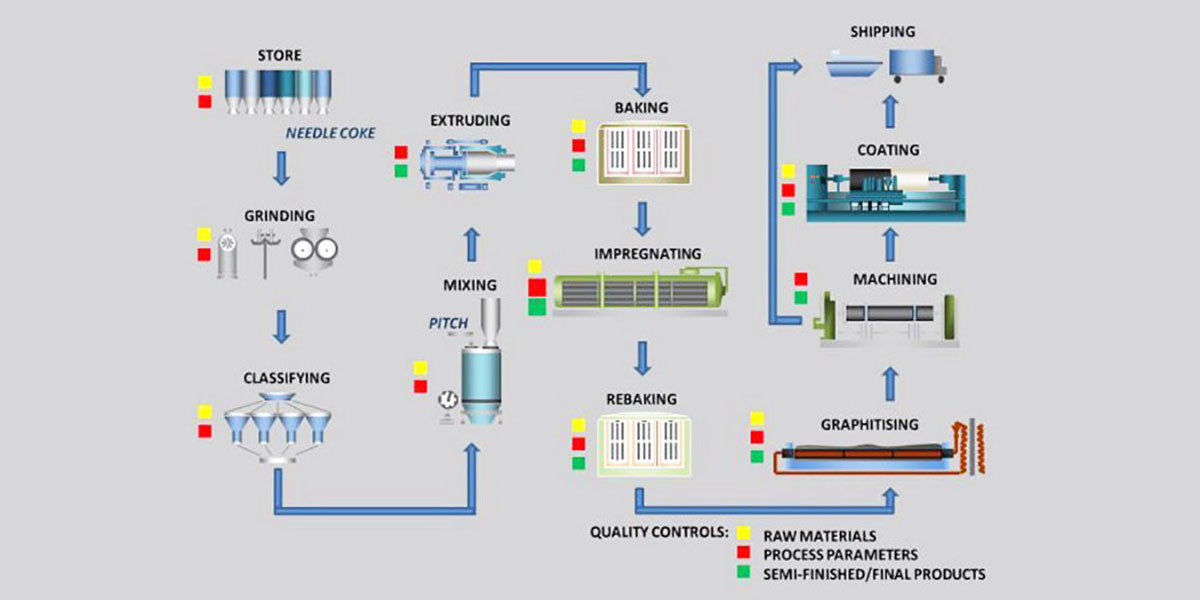
Graphite electrodes are made from petroleum coke after it is mixed with coal tar pitch.
They are then extruded and shaped, baked to carbonize the binder (pitch), and finally graphitized by heating it to temperatures approaching 3000 °C, at which the carbon atoms arrange into graphite.
Graphite electrodes are mainly used in electric arc furnaces.
They are presently the only products available that have high levels of electrical conductivity and the capability of sustaining the extremely high levels of heat generated in EAF. Graphite electrodes are also used to refine steel in ladle furnaces and other smelting processes.
Graphite electrodes are divided into 4 Types: RP Graphite electrodes, HP Graphite electrodes, SHP Graphite electrodes, and UHP Graphite electrodes.








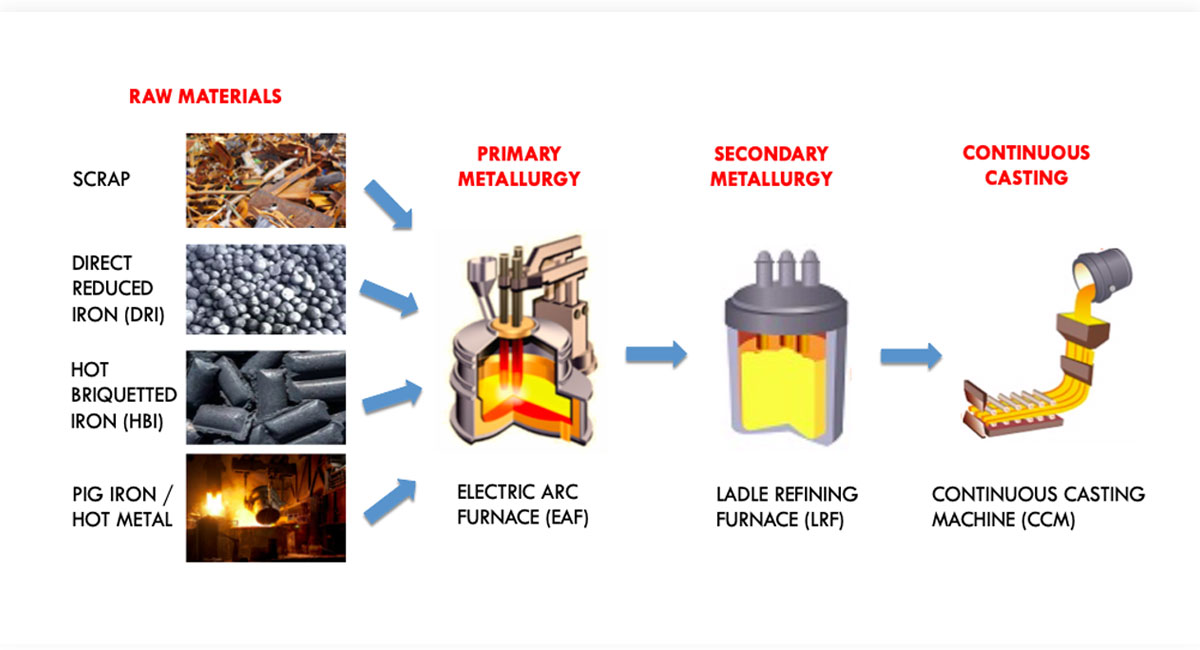
The graphite electrodes are primarily used to carry the electricity that melts scrap iron and steel in electric arc furnaces. As an increasing proportion of global steel is made using electric arc furnaces, the secondary production of steel becomes the major consumption of graphite electrodes. Additionally, the graphite electrode is also used in melting products in smelting furnaces, non-ferrous metals, ceramic products, and even the waste recycling industry. The demand for graphite electrodes is majorly dependent on its application in manufacturing steel through smelting by using an electric arc furnace (EAF). Steel manufacturers are shifting towards electric arc furnaces over the blast furnaces, owing to the advantages offered by EAF such as low cost of establishment, higher production flexibility, and low CO2 emissions.